Category: Science
While these are ‘close’ in astronomical terms, they’ll not even get within the orbit of the moon, but about 8 to 14 times farther away.
NASA Detects 5 Asteroids Flying Past Earth This Week.
NASA’s automated asteroid tracking system is monitoring five space rocks that will fly past Earth this week. Four of the approaching asteroids will enter Earth’s vicinity on the same day. Continue reading “”
Fun With Data: More ‘Research’ Blames Mass Shootings On Those Who Didn’t Do It
It’s time to play “spot the lousy gun research” again! There’s yet a new “study” out that purports to link high rates of firearm ownership to higher rates of mass shootings. It’s economically entitled Comparing the Impact of Household Gun Ownership and Concealed Carry Legislation on the Frequency of Mass Shootings and Firearms Homicide, by Emma E. Fridel.
I had to read this paper because the pseudo-news reports included a remarkable factoid.
In order to address these challenges, a unique dataset of all mass murders in the United States from 1991 to 2016 was created. …
To date, this represents the most comprehensive and accurate database available on mass shooting incidents in the United States, with a total sample size of 592 mass shootings during the study period.
Five hundred, ninety-two mass shootings? Gun Facts only found 94 from 1982 to 2019. The Violence Project lists 174 from 1966 to 2020. The Rockefeller Institute of Government identified 318 from 1966 to 2017.
Where did Fridel find hundreds more than any other researcher over a shorter time frame? The devil is in the definitions.
Rockefeller’s Capellan and Jiao defined “mass public shooting” as “the killing of four or more individuals in one or more closely related locations within a 24-hour period.” That’s representative of the definition usually used. It excludes targeted killings like gangbangers fighting over turf, or domestic disputes gone massively wrong.
It excludes serial shootings that don’t occur in a single incident. Fridel went with something a little different.
Defined as the killing of four or more individuals (excluding the offender) with a firearm within 24 hours… …
As WISQARS does not provide linkage information, firearms homicide was measured as a count of victims rather than incidents.
Four or more within 24 hours.
No gang or family exclusions. It doesn’t even necessarily specify that the four victims be shot for related reasons or even by the same shooter.
I’m sure she dinked around with that highly questionable definition until she got one that generated clusters in all the wrong states. Since she’s using WISQARS in part, I’m not even sure the “mass shooting” victims had to be in the same city or state, just the same 24 hour period.
Then I hit this.
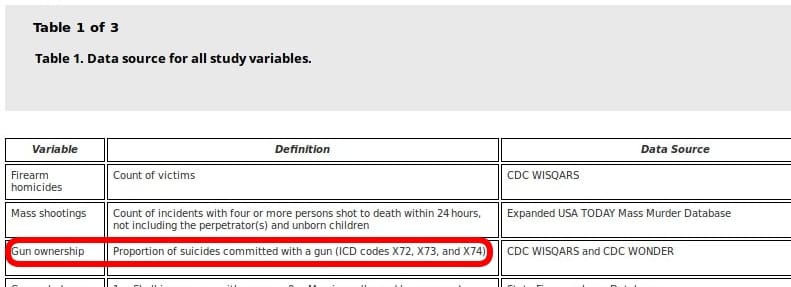
Household gun ownership was measured using a common proxy, the proportion of suicides committed with a firearm.
“Gun ownership” is estimated from suicides by firearm. Never mind that a goodly percentage of suicides are committed with firearms not owned by the subject. Never mind that better proxies, such as firearm hunting licenses, concealed carry licenses or in states like Illinois and Massachusetts, firearm owner licenses, exist.
Fridel gets to generate bogus data and reinforce the gun-ownership-equals-suicide canard, a twofer.
I should have quit there, but I was gripped by morbid curiosity.
She controlled her data for various socioeconomic and demographic factors. She included firearm homicide rates. But she specifically excluded non-firearm homicides, and violent crimes and property crimes.
It turns out she had per capita hunting license data, but decided not to use it; she just threw it out.
What this really is, then, is a study in how to manipulate and misuse data to further an agenda. Fridel could probably teach Garen Wintemute a few new tricks. Her data is so bad she probably wears an isolation suit to massage it.
When they come out with armored spacesuits, I’ll really get interested.
US Marines to get ‘Alpha’ exoskeleton for super strength.
The Marines are about to get their hands on an impressive bit of hardware: A wearable robotic exoskeleton that gives users super strength. The company delivering the unit, a defense-focused subsidiary of Sarcos Robotics developed the exoskeleton for industrial uses, including in energy and construction.
Still, in many ways, this is a return to roots for Sarcos. In 2000, the company was part of a storied class of DARPA grant recipients working on powered exoskeletons for defense purposes. In many ways, the XO, which conserves energy by remaining passive when not actuated, is the fulfillment of that research.
Another exoskeleton maker, Ekso Bionics, came out of the same DARPA grant.
According to Sarcos, the U.S. Marine Corps will test applications for its Guardian XO Alpha, which was first unveiled earlier this year at CES 2020, where it was named “Top Emerging Technology” by Digital Trends, “Best Robot” by PCMag.com, “The Best Ideas and Products of CES” by VentureBeat, and was recognized by WIRED Magazine as being one of the smartest technologies on the show floor. Although the suit may bring to mind nightmares of battlefield cyborgs, the more immediate applications will be in the realm of logistics, where heavy lifting is often necessary. Continue reading “”
BLUF: Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Carriers Are Not Very Contagious.
Background: An ongoing outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has spread around the world. It is debatable whether asymptomatic COVID-19 virus carriers are contagious. We report here a case of the asymptomatic patient and present clinical characteristics of 455 contacts, which aims to study the infectivity of asymptomatic carriers.
Material and methods: 455 contacts who were exposed to the asymptomatic COVID-19 virus carrier became the subjects of our research. They were divided into three groups: 35 patients, 196 family members and 224 hospital staffs. We extracted their epidemiological information, clinical records, auxiliary examination results and therapeutic schedules.
Results: The median contact time for patients was four days and that for family members was five days. Cardiovascular disease accounted for 25% among original diseases of patients. Apart from hospital staffs, both patients and family members were isolated medically. During the quarantine, seven patients plus one family member appeared new respiratory symptoms, where fever was the most common one. The blood counts in most contacts were within a normal range. All CT images showed no sign of COVID-19 infection. No severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections was detected in 455 contacts by nucleic acid test.
Conclusion: In summary, all the 455 contacts were excluded from SARS-CoV-2 infection and we conclude that the infectivity of some asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers might be weak.
“At first glance, a comparison of American violence and European violence is a prima facie case for stringent gun control. However, a closer examination of American violence reveals that it has little relationship to guns or gun policy.”
Israeli Professor Shows Virus Follows Fixed Pattern
Professor Yitzhak Ben Israel of Tel Aviv University, who also serves on the research and development advisory board for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, plotted the rates of new coronavirus infections of the U.S., U.K., Sweden, Italy, Israel, Switzerland, France, Germany, and Spain. The numbers told a shocking story: irrespective of whether the country quarantined like Israel, or went about business as usual like Sweden, coronavirus peaked and subsided in the exact same way. In the exact, same, way. His graphs show that all countries experienced seemingly identical coronavirus infection patterns, with the number of infected peaking in the sixth week and rapidly subsiding by the eighth week.
The Wuhan Virus follows its own pattern, he told Mako, an Israeli news agency. It is a fixed pattern that is not dependent on freedom or quarantine. “There is a decline in the number of infections even [in countries] without closures, and it is similar to the countries with closures,” he wrote in his paper.
“Is the coronavirus expansion exponential? The answer by the numbers is simple: no. Expansion begins exponentially but fades quickly after about eight weeks,” Professor Yitzhak Ben Israel concluded. The reason why coronavirus follows a fixed pattern is yet unknown. “I have no explanation,” he told Mako, “There are is kinds of speculation: maybe it’s climate-related, maybe the virus has its own life cycle.” ……..
Professor Yitzhak Ben Israel concludes in his analysis summary paper that the data from the past 50 days indicates that the closure policies of the quarantine countries can be replaced by more moderate social distancing policies. The numbers simply do not support quarantine or economic closure. ……….
While the American policies remain less restrictive than those of Israel, it is important to understand the origins of our own “mass hysteria” response. President Trump urged a strong coronavirus response after consulting with Dr. Fauci and his team, who relied on a British model predicting 2.2 million deaths in the United States and 500,000 deaths in the U.K. But that model was developed by Professor Neil Ferguson, who had a history of wildly overestimating death rates through his prediction models. ………
It’s been one month since our country declared a national coronavirus emergency and life as we knew it had ceased. Americans have been growing agitated, unwilling to continue in this way, knowing something is wrong. Trump has sensed that his constituency is displeased with the authoritarian power grab by our Governors and has repeatedly stated that he wishes to reopen the country, but that he needs more information to make the right decision. Professor Yitzhak Ben Israel’s data analysis provides Trump with the assurance that he needs to reopen America.
Come onnnnnnn Warp Drive.
New Earth-size planet discovered 300 light-years away could support life
A new, Earth-size exoplanet has been discovered in old data from NASA’s Kepler space telescope — and scientists say this world has the potential to support life.
The rocky exoplanet, known as Kepler-1649c, is only 1.06 times larger than Earth and is located about 300 light-years away, according to a new study released Wednesday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Out of all the exoplanets found by the now-retired Kepler space telescope, Kepler-1649c is the closest to our planet in size and estimated temperature.
The exoplanet orbits a red dwarf star within the so-called “habitable zone,” the area of space around a star in which liquid water could exist on a rocky world.
Researchers initially missed the planet when their computer algorithm misidentified it as a “false positive” while looking for planets in past Kepler space telescope observations. After double-checking the algorithm, scientists realized Kepler-1649c was, in fact, another world.
“Out of all the mislabeled planets we’ve recovered, this one’s particularly exciting,” said Andrew Vanderburg, a researcher at the University of Texas at Austin and an author on the study.
So, gun-grabbers lie. Like it’s not in their DNA or something?
‘Give me all you got‘? Okay, the citizen gots 5 rounds for ya.
Too bad he’s a bad shot….or the criminal is an out of work contortionist.
An armed man carjacked a motorist, robbed two businesses, and was shot at by a concealed carry holder whom he tried to rob — all within 15 minutes Thursday evening in Rogers Park, according to CPD reports. No one is in custody.
It all started around 9 p.m. when the offender displayed a gun in his waistband as he tried to rob Little Caesars, 7001 North Clark, the reports show. The man left empty-handed and immediately robbed Taqueria Hernandez across the street at 6983 North Clark.
At 9:04 p.m., the offender flashed a gun and carjacked a driver on the 1700 block of North Lunt, the reports said. He got away with the man’s silver 2008 Saturn sedan, which bears a license plate that begins with BK911.
But the gunman made a tactical error around 9:15 p.m. when he walked up to a concealed carry holder on the 7000 block of North Paulina, pulled out a gun, and said, “give me all you got.”
The would-be victim pulled out his own gun and opened fire on the offender, squeezing off at least five rounds at the man, officers reported. No one sought medical attention for gunshot wounds from nearby hospitals, so it appears the robber was not struck.
Police said the offender is a white man between 18- and 30-years-old who stands 5’9” to 6’2” tall, and weighs 160 to 200 pounds. He wore a black hoodie and a mask over the lower half of his face.
The concealed carry holder said the robber may have been Hispanic, according to details released by detectives late Friday. And the robbery victim on Lunt told police that the robber was accompanied by a black male who wore a camouflage mask.
I’ll just post this without any extraneous comment concerning the author’s sense of humor….or the lack of it.
- NASA’s Voyager 2 probe flew through a blob of charged gas called a plasmoid decades ago, and scientists only just now realized it.
- The blob could reveal secrets about the planet’s atmosphere loss, which may be related to its bizarre rotation and distinct wobble.
- Future missions near Uranus, or even to the planet’s surface, could reveal even more about its history.
First the anti-viral Remdesivir with hydroxychloroquine? Now the anti-retroviral Keletra? Each alone, maybe not too good, but apparently very effective in combination. Most promising
……. In a secret trial that was held, they were all given HIV medication, Kaletra and Malaria treatment hydroxychloroquine. The tests were truly successful that these drugs will now be rolled out to COVID-19 patients in at least 50 hospitals nationwide.
The drugs were very much effective
Scientists and researchers started to operate a secret trial on the group of patients who have all now completely recovered.
According to DailyMail, the Consultant Infectious Diseases Physician at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s and Hospital Clinical Research Director, Professor David Paterson of the University of Queensland Centre, have said that “These medications have the potential to be a real cure for all, unlike the random anecdotal experiences of some people.”
Paterson also said that the 50 hospitals will definitely try to resolve the best way to use these drugs and that this would involve comparing the two drugs separately and versus the combination of both.
On the same statement, Paterson reassures everyone that they are ready to go and quickly begin signing up patients into their trial, though this would only happen by the end of the month. The trial will then enable Paterson and his team to test the first wave of Australian patients.
These two drugs can be given orally as tablets
The federal government has already set aside $13 million for researchers to speed up potential treatments. These can be tested up o 10 treatments and with success, it will go directly through the regulatory approval process.
In France, they have begun using malaria drugs hydroxychloroquine in a small trial. Results only show 25% of tested patients treated with the drug still showed signs of the virus compared to a whopping 90% who did not use the drug.
In China, the active drugs in Kaletra, Lopinavir, and ritonavir, have already been tested in at least 199 patients with positive cases and found disappointing results. A published study in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 18 stated that the Chinese researchers gave 99 patients these drugs and the remaining had started care for more than four weeks.
The study concluded that hospitalized adult patients with severe cases had no benefit whatsoever with the drugs. This took 16 days for clinical improvements to arise. Although, the study did find that Kaletra spent the least time in intensive care….
Apollo 15 Astronaut Al Worden passes
Former astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot on the Apollo 15 lunar landing, passed away March 18, 2020, in Texas.
“I’m deeply saddened to hear that Apollo astronaut Al Worden has passed away,” NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine tweeted about Worden. “Al was an American hero whose achievements in space and on Earth will never be forgotten. My prayers are with his family and friends.”
As command module pilot, Worden stayed in orbit while commander David Scott and lunar module pilot James B. Irwin explored the Moon’s Hadley Rille and Appennine Mountains. Apollo 15’s command module, dubbed Endeavour, was the first to have its own module of scientific instruments. During the flight back from the Moon, Worden made three spacewalks to retrieve film from cameras in the module. Altogether, Worden logged more than 295 hours in space.
“The thing that was most interesting to me was taking photographs of very faint objects with a special camera that I had on board,” Worden told Smithsonian Magazine in 2011. “These objects reflect sunlight, but it’s very, very weak and you can’t see it from [Earth]. There are several places between the Earth and the moon that are stable equilibrium points. And if that’s the case, there has to be a dust cloud there. I got pictures of that.”
Like other command module pilots, Worden stayed as busy as his colleagues on the surface. But he also took some time to enjoy the view.
“Every time I came around the moon I went to a window and watched the Earth rise and that was pretty unique.”
After retirement from active duty in 1975, Worden became President of Maris Worden Aerospace, Inc., and was Vice-President of BF Goodrich Aerospace Brecksville, Ohio, in addition to other positions within the aerospace and aviation industries. Worden wrote several books: a collection of poetry, “Hello Earth: Greetings from Endeavour” in 1974; a children’s book, “I Want to Know About a Flight to the Moon”, also in 1974; and a memoir, “Falling to Earth,” in 2011. His interest in educating children about space led to an appearance on “Mr. Rogers’ Neighborhood”.
Worden was born Feb. 7, 1932, in Jackson, Michigan, on February 7, 1932. He was appointed to the United States Military Academy at West Point, graduating in 1955. He earned master of science degrees in astronautical/aeronautical engineering and instrumentation engineering from the University of Michigan in 1963. In 1971, the University of Michigan awarded him an honorary doctorate of science in astronautical engineering.
Before becoming an astronaut, Worden was an instructor at the Aerospace Research Pilots School. He had also served as a pilot and armament officer from March 1957 to May 1961 with the 95th Fighter Interceptor Squadron at Andrews Air Force Base, Maryland.
Worden was one of 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for Apollo 9 and as backup command module pilot for Apollo 12.
After leaving the astronaut corps, Worden moved to NASA’s Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California. He was the Senior Aerospace Scientist there from 1972-73, and then chief of the Systems Study Division until 1975.
The researchers also noted that more kids are killed each year in incidents involving pools and bicycles than in all the school shootings combined.
Of course, this study didn’t get a whole lot of attention in the mainstream media. That’s not surprising. After all, they seem to be personally invested in selling the idea that our kids aren’t likely to survive to graduate because of some maniac with an AR-15 is going to kill them all. Yet looking at the average over the last 25 years, it’s easy to see that more students are killed in car crashes than by mass shooters.
So why does everyone freak over these?
For one thing, it’s not about the total numbers. It’s about the number of people killed per incident. It’s not about how many have been killed in the last quarter of a century or what the annual average. If a dozen die in a single incident, that’s an even bigger tragedy but if you spread those deaths over an entire year, it’s a statistic.
That’s what’s fueling much of this nonsense.

Coronavirus up to 20 times more likely than Sars to bind to human cells, study suggests
That means ‘more contagious’.
- New strain appears to be more readily transmitted from human to human than Sars, Texas researchers find
- Further studies needed to explore human host cells’ role in spread between people, the report says
The deadly new coronavirus is up to 20 times more likely to bind to human cell receptors and cause infection than severe acute respiratory syndrome (Sars), a new study by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin has found.
The novel coronavirus and Sars share the same functional host-cell receptor, called angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).
The report, published on the website bioRxiv on Saturday, said the new coronavirus had around 10 to 20-fold higher affinity – the degree to which a substance tends to combine with another – for human ACE2 compared with Sars.
But the researchers added that further studies were needed to explore the human host-cell receptor’s role in helping the new virus to spread from person to person.
“Compared with SARS-CoV, 2019-nCoV appears to be more readily transmitted from human to human,” the report of the study said. “The high affinity of 2019-nCoV S for human ACE2 may contribute to the apparent ease with which 2019-nCoV can spread from human to human.”
The disease caused by the new coronavirus, which the World Health Organisation (WHO) has named Covid-19, has killed more than 1,800 people and infected over 70,000 worldwide.
The number of Covid-19 deaths is more than double the global figure of 813 attributed by the WHO to the Sars epidemic of 2002-03.
The new study found that although the novel coronavirus’ receptor-binding domain (RBD) had a relatively similar structure to that of Sars, it did not have appreciable binding to three published Sars RBD-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), which are copies of one type of antibody used to neutralise pathogens.
The researchers said this suggested antibody cross-reactivity – the extent to which different antigens appear similar to the immune system – may be limited between the two virus RBDs, meaning Sars-directed mAbs will not necessarily work against the new virus.
Instead, they identified the spike protein of coronaviruses, which is essential to gain entry into host cells during the infection process, as the most important target for vaccines, therapeutic antibodies and diagnostics.
“Due to the indispensable function of the [spike] protein it represents a vulnerable target for antibody-mediated neutralisation,” the report said. “Knowing the atomic-level structure of the spike will support precision vaccine design and discovery of antivirals, facilitating medical countermeasure development.”
The WHO has declared the outbreak a global public health emergency, making it the sixth incident to date to warrant that designation.
There are currently no specific treatments for the novel coronavirus but the WHO director general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said last week that the first vaccine may be available in 18 months.
Scientists announce ‘breakthrough’ atomic map of coronavirus
Washington (AFP) – US scientists announced Wednesday they had created the first 3D atomic scale map of the part of the novel coronavirus that attaches to and infects human cells, a critical step toward developing vaccines and treatments.
It came as the death toll from the COVID-19 virus jumped past 2,000, almost all of them in mainland China where 74,185 cases of infection have been confirmed since it first emerged in late December.
The team from the University of Texas at Austin and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) first studied the genetic code of the virus made publicly available by Chinese researchers, and used it to develop a stabilized sample of a key part called the spike protein.
They then imaged the spike protein using cutting-edge technology known as cryogenic electron microscopy, publishing their findings in the journal Science.
“The spike is really the antigen that we want to introduce into humans to prime their immune response to make antibodies against this, so that when they then see the actual virus, their immune systems are ready and loaded to attack,” UT Austin scientist Jason McLellan, who led the research, told AFP.
He added that he and his colleagues had already spent many years studying other members of the coronavirus family including SARS and MERS, which helped them develop the engineering methods required to keep the spike protein stable.
Their engineered spike protein is itself being tested as a potential vaccine by the NIH.
The team is sending the map of its molecular structure out to collaborators around the world so they can improve it by making it provoke a greater immune response.
The model can also help scientists develop new proteins to bind to different parts of the spike and prevent it from functioning, to treat those already infected. These are known as antivirals.
“This is a beautifully clear structure of one of the most important coronavirus proteins — a real breakthrough in terms of understanding how this coronavirus finds and enters cells,” said virologist Benjamin Neuman at the Texas A&M University-Texarkana, who was not involved in the work.
“The structure shows that although the spike is made of the three identical proteins, one flexes out above the rest, effectively giving the virus a longer reach,” he added.
A useful aspect of the structure for vaccine development is that it maps out the size and location of chains of sugar molecules the virus uses in part to avoid being detected by the human immune system, added Neuman.
Cryogenic electron microscopy uses beams of electrons to examine the atomic structures of biomolecules that are frozen to help preserve them.
Three scientists credited with developing the technology were awarded the 2017 Nobel prize in chemistry.
‘Significant breakthrough’ in race for coronavirus vaccine.
I hope it works out as advertised.
The scientist leading the UK’s research into a coronavirus vaccine says his team have made a significant breakthrough by reducing a part of the normal development time from “two to three years to just 14 days”.
Professor Robin Shattock, head of mucosal infection and immunity at Imperial College London, said he is now at the stage to start testing the vaccine on animals as early as next week with human studies in the summer if enough funding is secured.
He told Sky News: “Conventional approaches usually take at least two to three years before you even get to the clinic. And we’ve gone from that sequence to generating a candidate in the laboratory in 14 days.
“And we will have it in animal models by the beginning of next week. We’ve short-tracked that part. The next phase will be to move that from early animal testing into the first human studies.
“And we think with adequate funding we could do that in a period of a few months.”
Yellowstone’s Steamboat Geyser breaks eruption record, stuns scientists
Ah, just in case the scientists forgot. The Yellowstone Caldera is one of the largest volcanoes on the North American continent. Not that anyone can do anything about it, if it erupts again. Just me, but it appears that something’s “heating up” underneath.
If you’re headed to Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, there’s a good chance that visiting the park’s iconic geysers will be near the top of your to-do list. In 2019, tourists were treated to plenty of activity from the Steamboat Geyser, which is the tallest currently-active geyser on the planet.
That’s great news for parkgoers and perhaps even for the park itself, but with over 45 eruptions in 2019, the geyser’s highly active streak is leaving scientists scratching their heads. The geyser erupted a whopping 32 times in 2018 before ramping up even further this year.
The most famous geyser at Yellowstone, and perhaps the world, is Old Faithful. Old Faithful is famous for its incredibly predictable schedule of eruptions, which makes it perfect for visits from tourists. Steamboat is different, often going quiet for long stretches before eventually roaring back to life.
As NPR reports, Steamboat Geyser didn’t erupt at all in 2015, 2016, or 2017. Park visitors weren’t treated to an eruption for three full years. 2018 was different, and 2019 has seen even more activity from the geyser. But why? Researchers can only guess.
“It’s such a big geyser. And the bigger something is, the easier it is to study,” Michael Manga of the University of California, Berkeley, told NPR. “But it also captures people’s imagination. When it got active again there was lots of press and it reminded people that there are fundamental things about the Earth we don’t understand.”
Of course, you can’t mention Yellowstone’s geysers without also mentioning the suspected supervolcano resting beneath the park. Researchers believe that a massive volcano erupted in Yellowstone around 631,000 years ago. Scientists believe it will eventually erupt again, though estimates of when that might occur often conflict.
The gun control groups like to include all deaths through age 19 as children. Here are the 2016 breakdowns by category and age. Click to enlarge.
Accidental deaths (all firearms types)
Homicides (all firearms)
Suicides (all firearms)
None of these are wonderful, but notice that mostly these include the gang member age range: 15-19
